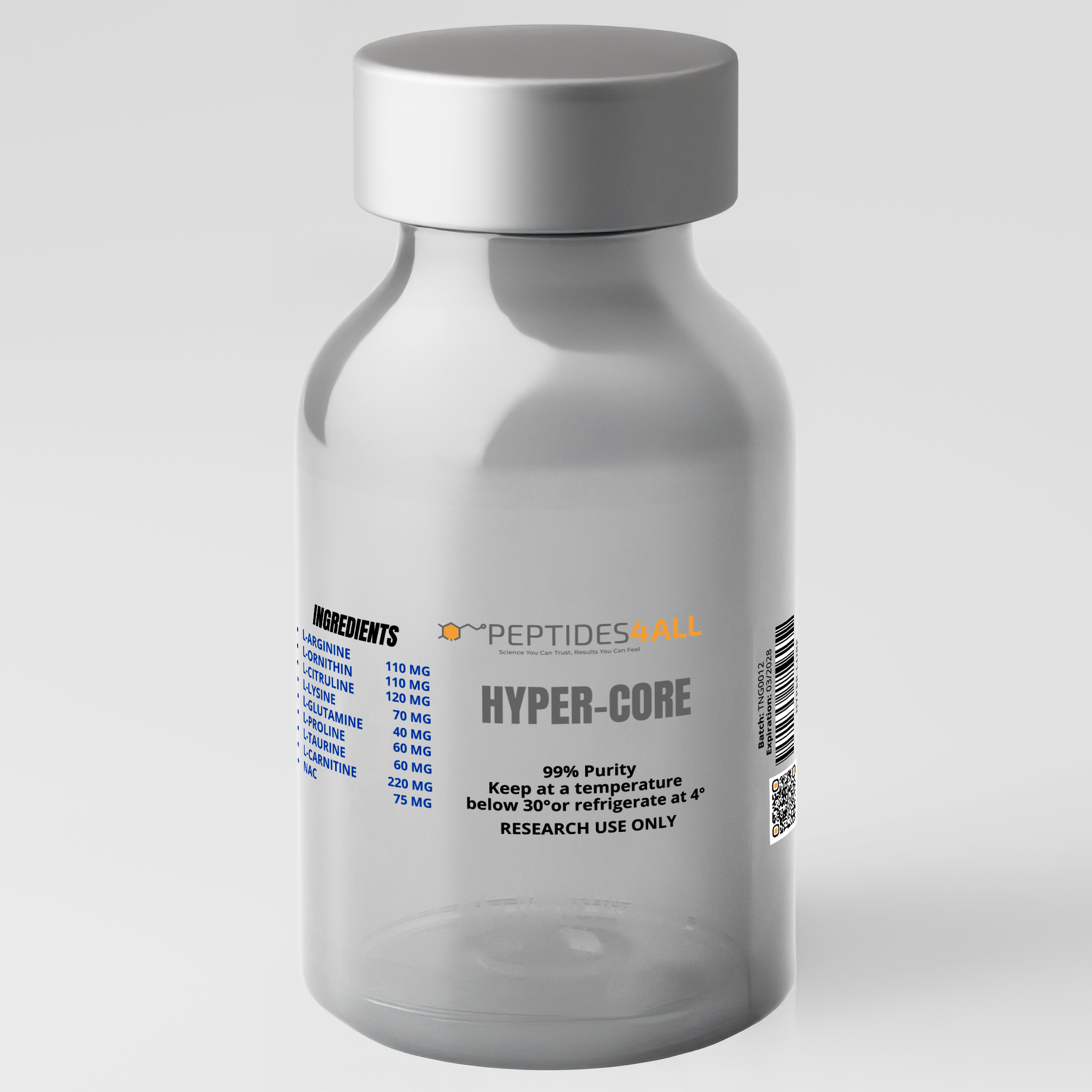
PEPTIDES4ALL HYPER-CORE – Intramuscular Performance & Recovery Amino Acid Blend
HYPER-CORE is a sterile intramuscular (IM) injectable blend designed for research use, combining a potent mix of amino acids and antioxidant precursors to support performance, recovery, nitrogen balance, vascular support, and detoxification pathways in experimental models. This blend is formulated to explore how amino acid synergy, nitric oxide modulation, and redox regulation may influence metabolic, muscular, and physiological outcomes under stress, exercise, or disease models.
Composition (per dose):
-
L-Arginine 110 mg
-
L-Ornithine 110 mg
-
VialL-Citrulline 120 mg
-
L-Lysine 70 mg
-
L-Glutamine 40 mg
-
L-Proline 60 mg
-
L-Taurine 60 mg
-
L-Carnitine 220 mg
-
N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) 75 mg
Scientific Evidence & Research Findings
Arginine, Citrulline, Ornithine — Nitric Oxide & Urea Cycle Support
-
L-Arginine is a precursor for nitric oxide (NO) production, contributing to vasodilation, improved blood flow, and nutrient delivery.
-
L-Citrulline is often used to boost systemic arginine levels more effectively, because it bypasses hepatic arginase and can be recycled via the citrulline–NO cycle. Several studies suggest combining arginine + citrulline may synergize to support performance outcomes. MDPI
-
In animal and human work, citrulline supplementation has been shown to upregulate PGC-1α in muscle, enhance mitochondrial biogenesis, and improve time to exhaustion in some models. PMC
-
A meta-review examined citrulline malate supplementation as an ergogenic aid, though results are mixed and dose/formulation dependent. PMC+1
-
Some human trials show citrulline may reduce perceived exertion or muscle soreness post-exercise. Human Kinetics Journals+1
L-Glutamine, NAC — Redox, Detox, & Recovery Support
-
NAC is a glutathione precursor and antioxidant, supporting redox balance, cellular defense against oxidative stress, and detoxification.
-
Studies of combined administration of glutamine + NAC have shown synergistic effects in modulating oxidative stress and cellular response. ScienceDirect
-
In cellular and reproductive biology research, NAC and L-carnitine have demonstrated antioxidant benefits (e.g. in sperm cryopreservation studies). ecerm.org+1
L-Carnitine, Taurine, Proline, Lysine — Energy, Osmoregulation, Structural Support
-
L-Carnitine plays a key role in mitochondrial β-oxidation (transport of fatty acids into mitochondria), potentially supporting energy output and lipid utilization. It is also cited in reviews of metabolic cofactors in health. PMC
-
Taurine is known to act as a natural antioxidant and modulator of cellular volume, osmoregulation, and membrane stabilization. MDPI
-
Proline is a critical amino acid in collagen synthesis and connective tissue health, complementing structural integrity in recovery contexts.
-
Lysine is essential for protein synthesis, supports collagen formation, and serves as a structural building block for growth and repair.
Key Research Benefits & Applications
-
Vasodilation & Perfusion: Arginine + citrulline synergy may enhance NO production and microvascular flow, supporting nutrient/oxygen delivery under stress or exercise.
-
Nitrogen Clearance & Urea Cycle: Ornithine, citrulline, and arginine interplay supports ammonia detoxification via urea cycle intermediates.
-
Mitochondrial Energy: Carnitine enhances fatty acid oxidation, while proline, glutamine, and lysine support substrate flux and repair.
-
Redox Resilience: NAC, glutamine, and taurine buffer oxidative stress and replenish antioxidant pools, aiding recovery and reducing cellular damage.
-
Structural Recovery: Lysine and proline aid in collagen formation and connective tissue repair, potentially beneficial in musculoskeletal recovery models.
Formulation, Handling & Storage
- Formulation: Sterile, preservative-free IM injectable solution
- Administration: Intramuscular injection (e.g. deltoid, gluteal) under sterile technique
- Storage: –20 °C, shielded from light and moisture; handle under lab protocols
Intended Use
For research purposes only. Must be handled in accordance with institutional protocols and ethical guidelines.